In Beta
AI Rental Agent
0→1 AI agent that increased conversions & reduced operator workload

I designed a fully transactional AI rental agent, treating AI behavior as a core design material rather than a UI layer.
By prototyping directly with LLMs and designing the conversational architecture, privacy model, and checkout flow, I enabled the system to safely capture leads, complete payments, and drive conversions under real-world constraints.
Product
web
Timeline
3 Weeks
Skills
End-to-end product design
AI interaction design
LLM prototyping
System logic + UX
My Rolle
Lead Designer
Team
AI Engenering Architect, Data PM
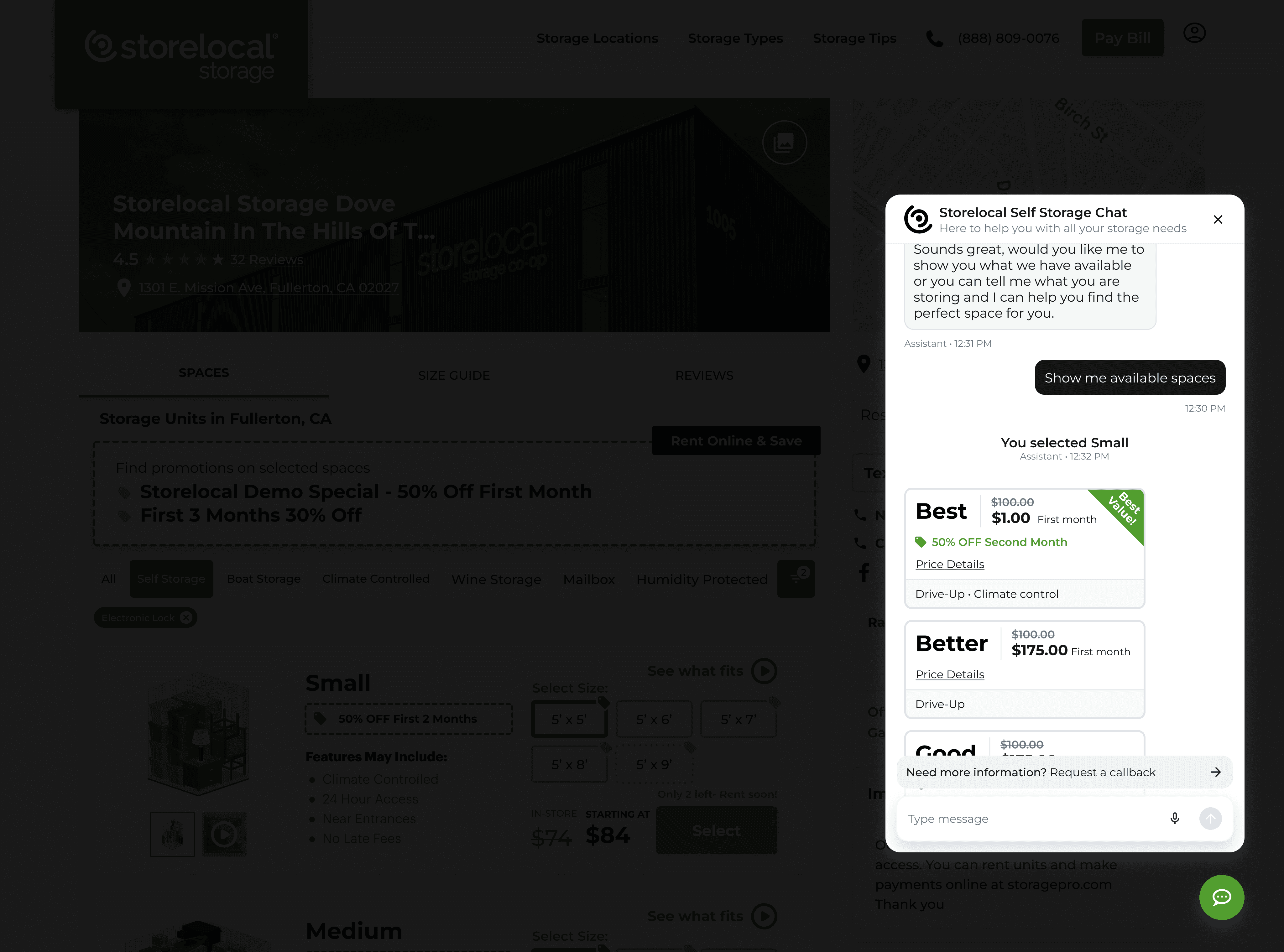


Overview
Context & Constraints
Self storage companies lose a significant portion of rental leads after hours. Existing chat solutions can answer questions, but fail when users attempt to complete real transactions—breaking trust and conversion.

Designing AI as a System
Chapter 1
LLM Prototyping as Design & Research

Challenge
Traditional UX flows break down with probabilistic LLM behavior. The challenge was designing an AI that could reliably interpret storage-specific intent, execute multi-step tasks, and drive revenue, not just respond.
Design Decision
I treated the LLM itself as a design prototyping tool. Before creating UI, I ran conversational experiments to test:
Industry-specific intent recognition
Sentiment detection
Multi-step task completion
Upsell timing and phrasing
This allowed me to validate feasibility before investing in interface design.
Outcome
By validating AI behavior first, the product foundation supported complex rental tasks, enabling a conversational system capable of completing bookings instead of simply answering questions. Targeting primary metrics
Intent resolution rate ↑
Successful outcomes per session ↑
Chapter 2
Designing for Trust, Privacy, & Flow
Challenge
Rental transactions require users to provide sensitive information, including payment details and personal data. Directly exposing this data to an LLM created security, compliance, and trust risks.
Design Decision
I designed custom UI widgets to securely capture sensitive inputs while implementing an event-based logging system that communicated completed actions to the AI without exposing raw data.
Trade-Off
This reduced conversational flexibility and removed some “natural chat” moments. However, it increased security, trust, and scalability.
Outcome
The AI could safely support payments and reservations while maintaining user confidence and meeting production-level privacy expectations.
Chapter 3
Conversational Product Architecture
Challenge
Traditional chatbots often break when users change topics, return later, or interrupt task flows. The system needed to support dynamic, multi-turn conversations while guiding users toward successful rental completion.
Design Decision
I designed a conversational architecture that mapped user intent to system actions while maintaining persistent conversational state. This included:
Intent-to-action routing
Context preservation across sessions
Anticipatory prompts that reduce decision friction
Escalation and fallback pathways
Trade-Off
Building structured conversational logic required additional system planning and reduced flexibility in fully open-ended chat. However, it improved reliability, clarity, and task completion rates.
Outcome
The AI functioned as a structured product system capable of guiding users from discovery through checkout while adapting to interruptions and returning users.
Chapter 4
Sales Without Being Pushy
Challenge
The AI needed to increase conversions and upsell storage units without creating intrusive or aggressive sales interactions that could damage user trust.
Design Decision
I modeled the AI’s conversational behavior after in-person retail experiences, introducing upsell opportunities only when users demonstrated purchase intent and offering lead capture options that remained optional and non-disruptive.
Trade-Off
This approach prioritized long-term trust and user comfort over maximizing short-term upsell exposure.
Outcome
The AI increased revenue opportunities while maintaining a supportive, customer-focused experience that encouraged users to continue interacting with the system.

ACT IV — The Solution
ACT II Overview
Context & Constraints

ACT II Overview
Context & Constraints

Business Impacts
By integrating directly with the marketplace and property management system, the AI has real-time access to inventory, pricing, and customer state; allowing it to act as a true rental agent, not just a support tool.
Conversions
Turns high-intent conversations into completed rentals by enabling discovery, reservation, and checkout directly in chat. Positions AI as a revenue-generating system—not just a support tool (Measured by payment link opens, payments completed, and move-ins via chatbot)
Lead Capture
Captures and nurtures qualified leads during live conversations, ensuring after-hours demand is not lost.
Operational Efficiency
Automates high-frequency rental tasks, reducing operator involvement and support load.
Customer Satisfaction
Maintains a high-quality experience by allowing users to complete tasks quickly while capturing feedback for continuous improvement. (Measured by thumbs-up / thumbs-down and qualitative feedback)
Platform Differentiation
Positions the AI as a category-defining rental agent within the industry, not just a chatbot—leveraging live marketplace and PMS data to complete bookings, process payments, and handle operational tasks that horizontal chatbots can’t match






